Please click below to watch DR.D.K.JHA discussing management of asthma in children in accordance with GINA guideline.
Year: 2021
INVASIVE PEDIATRIC MECHANICAL VENTILATION MADE SIMPLE BY DR.D.K.JHA,M.D.,Pediatric Pulmonologist and Respiratory Intensivist-Delhi
Please click below to watch DR.D.K JHA,talking invasive Pediatric Mechanical ventilation in a very simple and enjoying way
NEWER TESTS TO DETECT INFECTION WITH Mycobacterium Tuberculosis,Dr.Dev,M.D.,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Mohan Nagar,Ghaziabad,Delhi NCR
The oldest and time tested test to detect Tuberculosis infection in an individual is TST(Tuberculin skin test),also known as Mantoux test.It is being done with PPD RT -23.The standard strength for its use is 2TU(tuberculin unit).
But this strength is not available in the market and pathologists are compelled to use 5TU,the cut off value of induration for which is not standarized.
Moreover ,there may be false positive results, due to cross reactivity with Mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis (NTM)and BCG Vaccination particularly if the vaccination has been done after the infantile period.
The latest test which will be available in market very shortly is C-Tb skin test.
C-Tb skin test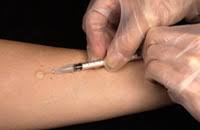
C-Tb test- This test is done in a similar manner as Mantoux test.Instead of PPD-RT23,in this test, antigens either ESAT6 or CFP 10 are used ,which are also used in Quaniferon Gold test.
This is the reason,it does not cross react with non tuberculous Myobacterium(NTM) as well as with BCG.At the same time, the test is not as complicated as Quantiferon Gold as it does not require sophisticated laboratory.
In the same way as in Mantoux test,0.1 ml of antigen is inoculated intradermally and the induration is meassured after 48-72 hours with ball pen and scale method. The cut off point has been established at 5mm for all age groups,irrespective of HIV status,irrespective of BCG Vaccine status.
The positive result indicates only the infection specifically to Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not the active disease
IGRA TEST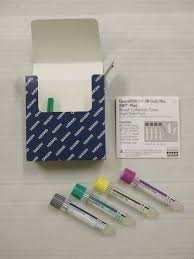
IGRA TEST:This test is interferon gamma release assay test.This is based on the principle that when T lymphocytes infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is exposed to specific antigen of M.Tb, in the form of either ESAT6 or CFP10 ,they release interferon gamma which is then measured.There are two tests,
QUANTIFERON TB GOLD ;In this test total interferon gamma which are released is measured
and
T spot TB. -It is a variant of Ellispot .In this test the number of effector T cells are measured which release interferon gamma upon exposure to specific antigens.
So ,this test is specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and it is not positive in cases of NTM(non tuberculosis mycobacteria) or in cases of BCG vaccination.
There is no need of a technique of intradermal inoculation and the measurement of induration as this test uses blood withrawn from patients.
There is no need of different cut off point of induration for HIV and non HIV patients
This test indicates only the infection,not the active disease
But ,this is not reliable below the age of 5 years.
REFERENCES:
1. World Health Organization. Guidelines on the management of latent tuberculosis infection. 2015. Report No.: WHO/HTM/TB/2015.01
2. Aggerbeck H, Giemza R, Joshi P, Tingskov PN, Hoff ST, Boyle J, et al. Randomised Clinical Trial Investigating the Specificity of a Novel Skin Test (C-Tb) for Diagnosis of M. tuberculosis Infection. PLoS ONE 2013;8(5):e64215 10.1371/journal.pone.0064215 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
3.Hoff ST, Peter JG, Theron G, Pascoe M, Tingskov PN, Aggerbeck H, et al. Sensitivity of C-Tb: a novel RD-1-specific skin test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection. Eur Respir J 2015. December 17;47(3):919–28. 10.1183/13993003.01464-2015 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
4.Ruhwald M, Aggerbeck H, Gallardo RV, Hoff ST, Villate JI, Borregaard B, et al. Safety and efficacy of the C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, compared with an interferon gamma release assay and the tuberculin skin test: a phase 3, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 2017. January 31;5(4):259–68. 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30436-2 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
5. World Health Organization. Guidance for national tuberculosis programmes on the management of tuberculosis in children – 2nd ed. 2014. Report No.: WHO/HTM/TB/2014.03.
…
6.C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children and HIV-infected adults: A phase 3 trial
PLoS ONE. 2018; 13(9)
7. Mori T, Sakatani M, Yamagishi F, Takashima T, Kawabe Y, Nagao K, et al. Specific detection of tuberculosis infection: an interferon-gamma-based assay using new antigens. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004. July 1;170(1):59–64. 10.1164/rccm.200402-179OC [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
8.Sollai S, Galli L, de MM, Chiappini E. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the utility of Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a 2013 update. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14 Suppl 1:S6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar
9.Sensitivity of C-Tb: a novel RD-1-specific skin test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection.
[Eur Respir J. 2016]
10.Safety and efficacy of the C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, compared with an interferon γ release assay and the tuberculin skin test: a phase 3, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial.
[Lancet Respir Med. 2017]
11.Review Gamma interferon release assays for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
[Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014]
12.Specific detection of tuberculosis infection: an interferon-gamma-based assay using new antigens.
Mothers infected with Coronavirus,may be protective to their newborn infants,Dr.D.K.JHA,M.D.,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Delhi

Coronavirus (SARS-Cov 2) infections causing Coronavirus disease(Covid 19) have killed many people worldwide since its spread starting from November 2019.
Vaccines are now available worldwide to protect the world populations by synthesising antibody in human body which fights and kills Coronavirus when it enters into the body.
Vaccines are not recommended currently for pregnant women as well as for infants and children.
In such scenario, if it is known that coronavirus infections stimulate the production of antibody against it and it is transferred from mothers to newborn infants to protect them,it will be gift to infants by nature.
In childrens hospital Philadelphia,1714 women were studied who delivered between April 9 to August 8,2020.
Immunoglobulin G(IgG) were measured from the serum of mothers and cord blood of their newborns in 1471 cases
SARS-CoV 2 antibody IgG were detected in 83 women,that is in 6% women.This IgG is known to cross the placenta.
Among these 83 women,72 newborns were detected to have IgG,that is in 87% cases.
No antibody was detected in newborns of seronegative mothers.
In 11 newborns of seropositive mothers,no antibody was detected.Among them,5 mothers were having only IgM ,which does not cross the placenta and 6 mothers were having very low titre of IgG.
So, it is very important study,which showed the presence of protective antibody in newborns of mothers who were infected with Coronvirus and produced protective antibody for themselves as well as for their newborn infants.
REFERENCES:JAMA Pediatrics,Published online on January 29,2021
Drug resistant Tuberculosis,What we know till beginning of 2021,DR.D.K.JHA,M.D.,Pediatric Pulmonologist,Delhi
Tuberculosis is very very old disease of human .
There has been many research in the field of diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis.
Inspite of all the efforts worldwide,it is still the killer disease due to various reasons responsible for the emergence of drug resistant TB (Tuberculosis).
Chief responsible factors for the increased incidence of tuberculosis are poverty leading to undernutrition, and HIV infection.
Main causes of emergence of drug resistance is not completing the prescribed regimen of treatment and high burden of tuberculosis.
TERMINOLOGIES BEING USED:
Monoresistant tuberculosis-Resistance of tuberculosis to any first line drug-Rifampicin,Isoniazid,pyrazinamide,ethambutol
Polyresistant tuberculosis: Resistance of tuberculosis to more than one drug but not to both Rifampicin and Isoniazid
Multi drug resistant(MDR) tuberculosis: Resistance to both Rifampicin and Isoniazid with or without resistance to other drugs
Pre-extensively drug resistant(PRE-XDR) tuberculosis:Resistance to both Rifampicin and isoniazid with resistance to either fluoroquinilones or second line injectables but not to both fluoroquinolones and second line injectables(SLI)
Extensively drug resistant tuberculosis(XDR):Resistance to Rifampicin,Isoniazid,fluoroquinolones and second line injectables(SLI)
RR-TB:Resistance to Rifampicin with or without resistance to other antituberculous drugs
SECOND LINE INJECTABLES(SLI):Amikacin,Kanamycin and capreomycin
PRIMARY RESISTANCE:When a child or adult becomes infected with drug resistant strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
SECONDARY/ACQUIRED RESISTANCE:This is more common.The individual is infected with drug sensitive strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis but it becomes drug resistant during treatment due to selection of resistant mutant strain.The cause of such resistance is incopmlete or suboptimal treatmen
TERMS USED IN DIAGNOSTIC PROCESSES
C-Tb skin test;This is a new test for the detection of tuberculosis infection.In this test ESAT6/CFP10 antigens are used.It is done in the same way as Tuberculin skin test(TST).Antigen is injected intradermally on the forearm and reaction is read after 48-72 hours with the ball pen-scale method.An induration of 5mm is taken as positive irrespective of age,BCG status and whether with HIV or non HIV.The sensitivity is comparable to TST(MANTOUX TEST) and IGRA(QUANTIFERON GOLD)
IGRA(QUANTIFERON TB GOLD IN TUBE TEST;QFT-GIT: AND T-SPOT TB TEST:T-SPOT):This test is based on the principle of white blood cells of individuals infected with mycobacterium release interferon gamma when mixed with antigens derived from Mycobacterium.In this test whole blood is taken from individual and then mixed to ESAT6/CFP10 antigens and result is available within 24 hours.It does not differentiate between active and latent Tb.This test is not affected by BCG vaccination and is specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not reliable below 5 years of age.
TESTS TO DETECT MYCOBACTERIUM:
LAMP;Loop mediated isothermal amplification test is 15% more sensitive than Zeil Neilson microscopy(smear microscopy) which is most widely used traditional test to detect Mycobacterium in smear preparation of sample in the form of sputum or gastric aspirate. It is temperature independent test ,done manually for amplification of DNA and can be read by naked eye with ultraviolate light.The report is available within one hour.WHO has recommended it as an alternative to ZN microscopy as it can be used in periphery
LED-FM:Light emitting diode fluorescent microscopy is 10 % more sensitive than ZN microscopy.With proper training it can be used in periphery although its specificity is less.WHO has recommended it as an alternative to ZN microscopy.According to WHO policy paper its sensitivity is 86.3%
CBNAAT :Cartridge based nucleic acid amplification test is based on polymerase chain reaction for the ampilification of DNA.Report is available within 2 hours.It can detect live as well as dead tuberculous bacilli ,so it can not be a replacement for smear microscopy and culture based drug sensitivity test for folllow up.It is also known as GenXpert /Rif test.It also detects Rifampicin resistance.Its sensitivity is 89% and specificity is 99%
GenXpert ultra(CBNAAT ULTRA):It is an advance version of GenXpert which is ultrasensitive with main difference from GenXpert is ,it can detect Mycobacterium from sputum even if the number of bacilli per ml is as low as 16,whereas in GenXpert ,the number of bacilli should be 131/ml for detection
TRUENAT;It has been developed in India by Molbio Diagnostics Pvt.Ltd.Goa.Its sensitivity and specificity to detect Mycobacteria and Rifampicin resistance is similar to CBNAAT/GenXpert test.But it requires 0.5 ml of sample as compared to CBNAAT which requires 1 ml.It is battery operated and not fully automated so it does not require continuous power supply and can be used in periphery


LPA-Line probe assay is based on polymerase chain reaction with reverse hybridization technique.First line assay detects resistance to isoniazid while second line LPA detects resistance to Fluoroqinolones and SLI.Report is available within 24-48 hours.According to recent RNTCP guideline,if Rifampicin resitance is detected on CBNAAT,second sample is sent to detect isoniazid resistance by LPA.If isoniazid resistance is detected,second line LPA is done for Fluoroquinolones and SLI.If Rifampicin sensitivity is detected on CBNAAT,sample is sent for LPA to detect isoniazid resistance.
According to WHO,END TB Programme,all patients should be subjected to DST(Drug sensitivity test) and the reference standard for this test is either liquid or solid culture.The report becomes available in 12 weeks.
To meet the requirement of universal DST as recommended by WHO,rapid tests are being developed as-NEXT GENERATION SEQUENCING(NGS).It is a rapid molecular test to detect mutations responsible for drug resistance.These are of 3 types
Targeted NGS-it sequences the specific point on gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Whole genome sequencing(WGS)It sequences the whole genome ,so it is better than TNGS.
Pyrosequencing-it is method of sequencing by synthesis.
DRUGS TO TREAT RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS:
GROUP-A-Levofloxacin or Moxifloxacin,Bedaquiline,Linezolid
GROUP-B-Clofazimine,Cycloserine or Teridizone
GROUP-C-Ethambutol,Delamanid,Pyrazinamide,Imipenam-cilastin or Meropenam,Amikacin or Streptomycin,Ethionamide or Prothionamide,Para-Aminosalicylic acid(PAS)
There are TWO regimens for the treatment of drug resistant tuberculosis,Long course and Short course
Long course is for 18-20 months-According to WHO 2019 guideline, 2 drugs from Group A except Bedaquiline in children,1-2 drug from Group B along with Delamanid must be chosen and the list of at least 5 drugs is completed from Group C.After 6 months of continuation phase,Delamanid is withdrawn and at least 4 drugs should be continued for the rest of the period of treatment..
DELAMANID CAN BE GIVEN TO CHILDREN ABOVE 3 YEARS OF AGE
SHORT COURSE REGIMEN:It is given for a period of 9-12 months.Usually the intensive phase is of 4-6 months consisting of Moxifloxacin,high dose isoniazid,ethambutol,,pyrazinamide,clofazimine,ethionamide or prothionamid,Kanamycin or Amikacin(7 drugs) followed by a fixed period of 5 months of Moxifloxacin,clofazimine,pyrazinamide and ethambutol(4 drugs)
Drug resistance to Fluoroquinolones and second line injectables should be ruled out before initiating short course treatment.
Now a days it is being emphasised and WHO in June 2020 has recommended ,all oral drug regimen where injectables shuold be replaced by Bedaquiline.FDA has approved Bedaquiline above 12 years of age but in India it has been approved above 18 years in accordance to RNTCP guideline.
NOTE:High dose isoniazid- dose is 15-20 mg/kg/day-it can cause optic and peripheral neuritis,ANA positivity,agranulocytosis,vasculitis and thrombocytopenia.
Linezolid-Dose 15 mg /kg od for wt<15 kg and 10-12 mg/kg od,for >15kg.It causes Myelosuppression,peripheral and optic neuritis and lactic acidosis.It penetrates CNS well
Ethionamide/Prothionamide causes hypothyroidism
EPTB and CNS Tb should be treated with longer regimen
REFERENCES:
TB facts.GenXpert Test-TB diagnosis,TB resistance testing,CBNAAT.2018.Available at:http://www.tbfacts.org/genexpert/Accessed
2019
World Health Organisation(WHO).The use of next generation sequencing technologies for The detection of mutations Associated with drug resistance in Mycobacterium toberculosis Complex;Technical guide.Available at http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/27443.Accessesd2019.
World Health Organisation.WHO consolidated guideline on Drug Resistasnt tuberculosis treatment 2019?Available at :https:apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/311389/9789241550529-eng.pdf.Accessed 2019
TERMS USED TO DESCRIBE RESISTANT TUBERCULOSIS,Dr.Dev,M.D.,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Mohan Nagar,Ghaziabad,Delhi NCR
The burden of resistant tuberculosis is on the rise which is a threat to WHO END Tuberculosis programme .
Children are also becoming victim but data are not sufficient yet
Primary resistance:When an individual is infected with resistant strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Secondary resistance:When an individual is infected with drug sensitive strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis but during the course of treatment the organism acquire resistance due to suboptimal treatment,incomplete treatment with high bacterial load.It is also known as acquired resistance.
MONORESISTANCE:When the organism is resistant to only one drug
POLYRESISTANCE;When the organism is resistant to 2 drugs but not to both Rifampicin and Isoniazid
MULTI DRUG RESISTANCE(MDR): When there is resistance to both Rifampicin and Isoniazid
PRE EXTENSIVELY RESISTANCE(PRE-XDR):When there is resistance to Rifampicin,Isoniazid with resistance to either Fluoroquinolones or Second line injectables(SLI) but not to both.
EXTENSIVELY DRUG RESISTANCE:When there is resistance to Rfampicin ,Isoniazid and both Fluoroquinolones and SLI
RR Tb: When there is resistance to Rifampicin with or without resistance to other anti tuberculosis drug
SLI(second line injectables): Amikacin,Kanamycin and Capreomycin
REFERENCES:Indian Journal of Pediatrics,volume 87/number 10/October 2020
Tips to maintain good appetite in children,Dr.Dev,M.D.,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Mohan Nagar,Sahibabad,Ghaziabad,Delhi NCR

A good appetite is gift of nature to every individual born on the planet.
As soon as the child is born ,he or she is hungry to take feeds.
Any child may not remain without taking feeds for a long time.
If the child is not hungry ,it is not natural.
A child with less appetite or loss of appetite is definitely suffering from some problems,either physical or psychological.
TIPS TO MAINTAIN APPETITE:
Do not feed the child very frequently as this practice inhibits the appetite centre of brain ,because you are not allowing time for this centre to be stimulated by hunger .
So, child should be given foods after a minimum gap of 2-3 hours.
Child should be given foods of their choice not of the choice of family members.
Child should never be forced to feed at a certain point of time if he or she is not interested to take feed at that time.
The food items should be well grinded so that any child may not have difficulty in manipulating it inside the mouth.
The child should be involved in outdoor play as long as possible so that their activities could be maximised which maintains the appetite.
There are some foods especilally zinc containing foods which increases the appetite.
These are -nuts like peanuts,almonds
Seeds like sesame seeds,pumpkin seeds
Cheese contains good amount of zinc.Beans contain good amount of zinc.
Child should be given foods with Indian spices in good quantity which increases appetite.
Every child should be exposed to household foods between the age of 6-12 months because this is the time of developing taste buds.By doing so,they will accept household foods in future during entire childhood period ,otherwise they will be more interested in foods from markets.
Child after the age of 1 year shuold not drink more than 500 ml of milk per day ,otherwise they will not be able to take the necessary elements as their stomach will be full of milk.
If the child is not interested in drinking milk,there is no problem,give them milk products like yoghurt ,cheese ,paneer which will meet the requirement as well as increase the appetite.
Never give tea or coffee to any child
DO not give fruit juices to children,instead give whole fruit after proper cutting or mashing as per the age of the child.
Avoid giving more oily foods as it may lower the appetite.
Loss of appetite is the feature of many diseases.So consult your doctor if the problem of less appetite persists.
Do not overfeed the child as it will increase the weight above the normal range making your child overweight or obese which is as bad as loss of weight.
NOTE; EVERY CHILD SHOULD BE GIVEN ONLY AND ONLY THE MILK OF MOTHER TILL THE AGE OF 6 MONTHS.
USUAL SYMPTOMS,UNUSUAL DIAGNOSIS,A CASE REPORT,Dr.Dev,M.D.,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Mohan Nagar,Sahibabad,Ghaziabad,Delhi NCR
 11 years old female child presented to our clinic with complaints of
11 years old female child presented to our clinic with complaints of
Fever for 24 days,
cough for 15 days
less appetite for 10 days
pain abdomen for 7 days
headache for 5 days
swelling of both lower limbs for 3-4 days
On examination;
Temperature 103 dF,pallor +,icterus+
Pulse rate 56/m regular(relative bradycardia)
Respiratory rate 26/minute ,regular
Generalised lymphadenopathy
bilateral pedal edema
Abdomen-not distended,no tenderness,hepatosplenomegaly+
Chest-bilateral equal breath sound,bilateral vesicular breath sound,bilateral crackles
CVS-NAD
CNS-NAD
Following diagnoses were suspected
Malaria
Typhoid
Viral hepatitis with secondary bacterial infection
Disseminated tuberculosis
Leptospirosis
Scrub typhus
Investigations were planned and done accordingly.
Hb 9 gm/dl
TLC 6800/cmm,P56,L34,E03,M07,B00,Platelet 90000/cmm
SGPT-102,SGOT146,ALP 200,S.BIL 3.8mg/dl
Serum Sodium 130mE/L,Serum potassium 4.4mE/dl
Serum widal-negative
Malaria antigen-negative
Chest X-Ray -bilateral reticulonodular opacities with bilateral pleural effusion
Mantoux test-negative
GA for CBNAAT -negative
The child was emperically treated as enteric fever with cefixime but there was no response.Then the child was treated emperically for malaria and again there was no response.
At this point of time,it was suspected that the child may be suffering from scrub typhus as the child travelled to Uttrakhand during last month.
IgM ELISA for scrub typhus was sent and it came to be positive and the child responded well to doxycycline.
DISCUSSION
:Rickettsia is intracellular ,gram negative proteobacteria with coccobacillar shapes.The disease caused by it is called Rickettsiosis.It is a zoonosis ,transmitted into human by mites(chiggers),ticks or fleas and rodents. Humen are the incidental host.No human to human transmission has been observed.
This disease is frequently seen in Uttrakhand,Rajsthan,assam.West Bengal ,Jammu and Kashmir,Maharashtra Tamil Nadu and Kerala region of India and many countries out of India.
pathogens causing disease in human have been broadly classified into three groups
1.Spotted fever group
2.Typhus group
3.Scrub typhus group
Scrub typhus is causing a health impact in Asia
Pathogenesis;The principle pathogenetic mechanism is vasculitis involving medium and small vessels.It causes increased vascular permeability by disrupting the endothelial tight junctions due to the bacterial load and tumour necrosis factor.Main cause of mortality is pulmonary edema and cerebral edema.
CLINICAL FEATURES OF SCRUB TYPHUS WHICH IS COMMON IN INDIA:
The usual incubation period is 10-12 days with a variability of 6-21 days.Symptoms varies from mild self limiting to severe causing death.
After the period of approximately 5-6 days of bite by mites,there occurs the formation of ESCHAR(shown in the figure) at the site of inoculation of the mite.It is a painless necrotic lesion over skin resembling a cigarette burnt skin surface.The usual sites are groin,axilla,back,neck and other exposed parts of the body.Eschar, if visibl,e makes a clear cut diagnosis of scrub typhus without any investigation.But it is not ususally seen in children.Its prevalence varies from 7-80%.
After about 5-7 days flu like symptoms occurs.In most of the cases fever has been observed with severe headache.
There may be myalgia,weakness,pain abdomen,vomiting,diarrhoea,cough.
O/E There may be relative bradycardia,generalised lymphadenopathy,generalised body rashes and pedal edema
On systemic examination:there may be hepatosplenomegaly
On investigation:
BLOOD-there may be anemia,thrombocytopenia,raised liver enzymes,raised serum bilirubin,hyponatremia,raised blood urea and serum creatinine
Chest X-Ray may show reticulonodular opacities,features of pulmonary edema,bilateral pleural effusion
ECG may shows features of myocarditis with nonspecific ST-T changes,features of heart block
LUMBAR PUNCTURES :CSF pictures are indicative of meningoencephalitis.The CSF picture is similar to Tuberculous meningitis with lymphocytic pleocytosis and raised protein.
DIAGNOSIS; The gold standard is INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORECENT ANTIBODY TEST(IFA), but it is not available everywhere.The next best is IgM ELISA which is widely available and should be done as the sensitivity of Weil-Felix test is very poor.
TREATMENT.The drug of choice is doxycycline,oral or i.v. in the dose of 2.2 mg/kg 12 hourly below 40 kg of weight and 100 mg b.d. above 40 kg of weight,for a period of 7 days of 3 days after the fever subsides.Now it has been recommended for children of any age to treat Rickettsial diseases as it has not caused enamel hypoplasia or teeth staining even after multiple courses.
Alternative medicine is Azithromycin in the dose of 10 mg/kg/day
Other drugs which may be used in special cases are -clarithromycin.chloramphanicol and Rifampicin
Mortality is above 50% if not recognised and treated timely
COMPLICATIONS.HLH(hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and it is very serious complication.
REFERENCES:
AbdadMY,Abou AbdallahR,FoumierP-E,StenosJ,Vasoo S.Aconcise review of the epidemiology and diagnostics of rickettsioses:Rickettsia and Orientia spp.J clin Microbiol.2018;56:eo1728-17
IssacR,VargheseGM,MathaiE,et al.Scrub typhus:prevalence and diagnostic issue in rural southern India.Clin infect dis.;2004:39;1395-6
Rathi N ,Kulkarni A ,Yewale V;Indian Academy of Pediatrics Guidelines on Rickettsial diseases in children committee.IAP Guideline on Rickettsial disesase in children.Indian Pediatr.2017;54:223-9
Elisabeth BN,Cristina S,DidIer R,Phillipe P.Treatment of Ricketssial spp.infections:a review.Exp rev anti infect Ther.2012;10:1425-37
NASAL POLYP,WORKING KNOWLEDGE,Dr.DEV,M.D,Pediatrician and Pediatric Pulmonologist,Mohan Nagar,Sahibabad,Ghaziabad,Delhi NCR
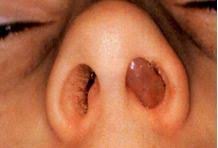 Nasal polyp is not uncommon in children and parents often get afraid of it when it is visible.
Nasal polyp is not uncommon in children and parents often get afraid of it when it is visible.
It is rare below the age of 10 yeras.
It is an abnormal growth which is semitransparent and may arise from any portion of nasal mucosa or epithelium of paranasal sinuses usually at its outflow.
Contrary to the common belief,it is associated more commonly with non allergic than allergic conditions.
It is seen more commonly in children with non allergic asthma than allergic asthma
It may be single or multiple depending on etiology.
CLINICAL FEATURES:
Small polyps are asymptomatic which are usually discovered during nasal examination for other causes,when they are located anterior to the anterior edge of middle turbinate
Symptoms depend on size and location of the polyp.
Small polyp arising from middle meatus may produce symptoms by blocking the outflow tract,causing chronic and recurrent sinusitis.
common symptoms are
Rhinorrhoea,
post nasal drip
facial pain
headache
toothache
hyposmia,
anosmia,
loss of taste,
blocked nose,
snoring.
When the size becomes large,it may cause obstructive sleep apnea
DIAGNOSIS;
Clinical examination is sufficient for the idendification of this lesion.Anterior rhinoscopy wll defines it.
Non contrast CT scan of nasal and paranasal sinuses are required to see the extent of lesions as in rare circumstances there may be malignant lesions.SO the imaging investigation of choice is non contrst CT scan.
CAUSES:
It arises due to chronic inflammation of nasal or paranasal mucosa,so it is commonly seen in children with allargic or non allergic rhinitis or sinusitis.
Multiple polyps are seen in children with cystic fibrosis,primary ciliary dyskinesia ,asthma and allergic fungal sinusitis.
TRATMENT:
Treatment is medical in most of the cases.Surgery is required only rarely when medical treatment fails.
In most of the cases ,short term oral corticosteroid and or intranasal steroid is needed.
REFERENCES:
Bernstein JM, Gorfien J, Noble B. Role of allergy in nasal polyposis: a review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995 Dec. 113 (6):724-32. [Medline].
Tos M, Sasaki Y, Ohnishi M, Larsen P, Drake-Lee AB. Fireside conference 2. Pathogenesis of nasal polyps. Rhinol Suppl. 1992. 14:181-5. [Medline
Rudmik L, Schlosser RJ, Smith TL, Soler ZM. Impact of topical nasal steroid therapy on symptoms of nasal polyposis: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2012 Jul. 122 (7):1431-7. [Medline].
Lund VJ, Flood J, Sykes AP, Richards DH. Effect of fluticasone in severe polyposis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1998 May. 124 (5):513-8. [Medline
Rudmik L, Schlosser RJ, Smith TL, Soler ZM. Impact of topical nasal steroid therapy on symptoms of nasal polyposis: a meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2012 Jul. 122 (7):1431-7. [Medline].