12 years female child visited me with the complaint of single episode of hemoptysis.
There was no history of fever,no history of cough other than the present single episode of cough.
There was no history of loss of appetite or weight loss in last 3 months
There was no contact with Tuberculosis patient in past 2 years
On examination -The anthropometry was appropriate for the age,General physical examination was normal
On systemic examination- Chest on auscultation revealed deep inspiratory crackles over right mammary region
On investigation-Chest X-ray showed consolidation in the right mid zone
Montoux test was non reactive,CBC was non contributory
There was no cough after that single episode so sputum could not be collected and nothing came after induced sputum.
The child did not allow gastric aspiration even after counselling.
Coagulation profile was normal
At this time I planned bronchoscopy to look for the region of hemoptysis.
On bronchoscopy,there was a clot in right bronchus intermedius and collected BAL fluid
BAL fluid was sent for CBNAAT and it came positive for Mycobacterium tubrculosis which was sensitive to Rifampicin
ATT was started from DOTS centre and the child id doing well.
This is the unusual presentation of tuberculosis in children with a single episode of cough with hemoptysis and no other symptoms.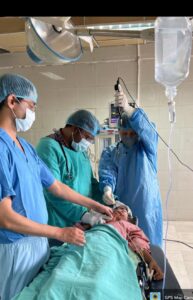
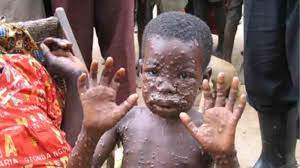 As the name suggests,this disease comes in human from animal,so it is called a zoonotic disease
As the name suggests,this disease comes in human from animal,so it is called a zoonotic disease It is very difficult to predict the course of asthma in children.
It is very difficult to predict the course of asthma in children. Asthma is the most common chronic disease in children.
Asthma is the most common chronic disease in children.