The oldest and time tested test to detect Tuberculosis infection in an individual is TST(Tuberculin skin test),also known as Mantoux test.It is being done with PPD RT -23.The standard strength for its use is 2TU(tuberculin unit).
But this strength is not available in the market and pathologists are compelled to use 5TU,the cut off value of induration for which is not standarized.
Moreover ,there may be false positive results, due to cross reactivity with Mycobacteria other than Mycobacterium tuberculosis (NTM)and BCG Vaccination particularly if the vaccination has been done after the infantile period.
The latest test which will be available in market very shortly is C-Tb skin test.
C-Tb skin test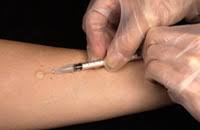
C-Tb test- This test is done in a similar manner as Mantoux test.Instead of PPD-RT23,in this test, antigens either ESAT6 or CFP 10 are used ,which are also used in Quaniferon Gold test.
This is the reason,it does not cross react with non tuberculous Myobacterium(NTM) as well as with BCG.At the same time, the test is not as complicated as Quantiferon Gold as it does not require sophisticated laboratory.
In the same way as in Mantoux test,0.1 ml of antigen is inoculated intradermally and the induration is meassured after 48-72 hours with ball pen and scale method. The cut off point has been established at 5mm for all age groups,irrespective of HIV status,irrespective of BCG Vaccine status.
The positive result indicates only the infection specifically to Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not the active disease
IGRA TEST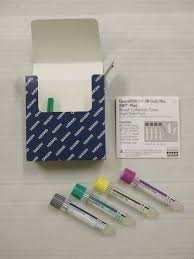
IGRA TEST:This test is interferon gamma release assay test.This is based on the principle that when T lymphocytes infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis is exposed to specific antigen of M.Tb, in the form of either ESAT6 or CFP10 ,they release interferon gamma which is then measured.There are two tests,
QUANTIFERON TB GOLD ;In this test total interferon gamma which are released is measured
and
T spot TB. -It is a variant of Ellispot .In this test the number of effector T cells are measured which release interferon gamma upon exposure to specific antigens.
So ,this test is specific for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and it is not positive in cases of NTM(non tuberculosis mycobacteria) or in cases of BCG vaccination.
There is no need of a technique of intradermal inoculation and the measurement of induration as this test uses blood withrawn from patients.
There is no need of different cut off point of induration for HIV and non HIV patients
This test indicates only the infection,not the active disease
But ,this is not reliable below the age of 5 years.
REFERENCES:
1. World Health Organization. Guidelines on the management of latent tuberculosis infection. 2015. Report No.: WHO/HTM/TB/2015.01
2. Aggerbeck H, Giemza R, Joshi P, Tingskov PN, Hoff ST, Boyle J, et al. Randomised Clinical Trial Investigating the Specificity of a Novel Skin Test (C-Tb) for Diagnosis of M. tuberculosis Infection. PLoS ONE 2013;8(5):e64215 10.1371/journal.pone.0064215 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
3.Hoff ST, Peter JG, Theron G, Pascoe M, Tingskov PN, Aggerbeck H, et al. Sensitivity of C-Tb: a novel RD-1-specific skin test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection. Eur Respir J 2015. December 17;47(3):919–28. 10.1183/13993003.01464-2015 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
4.Ruhwald M, Aggerbeck H, Gallardo RV, Hoff ST, Villate JI, Borregaard B, et al. Safety and efficacy of the C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, compared with an interferon gamma release assay and the tuberculin skin test: a phase 3, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Respir Med 2017. January 31;5(4):259–68. 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30436-2 [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
5. World Health Organization. Guidance for national tuberculosis programmes on the management of tuberculosis in children – 2nd ed. 2014. Report No.: WHO/HTM/TB/2014.03.
…
6.C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children and HIV-infected adults: A phase 3 trial
PLoS ONE. 2018; 13(9)
7. Mori T, Sakatani M, Yamagishi F, Takashima T, Kawabe Y, Nagao K, et al. Specific detection of tuberculosis infection: an interferon-gamma-based assay using new antigens. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004. July 1;170(1):59–64. 10.1164/rccm.200402-179OC [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
8.Sollai S, Galli L, de MM, Chiappini E. Systematic review and meta-analysis on the utility of Interferon-gamma release assays for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in children: a 2013 update. BMC Infect Dis 2014;14 Suppl 1:S6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar
9.Sensitivity of C-Tb: a novel RD-1-specific skin test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis infection.
[Eur Respir J. 2016]
10.Safety and efficacy of the C-Tb skin test to diagnose Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, compared with an interferon γ release assay and the tuberculin skin test: a phase 3, double-blind, randomised, controlled trial.
[Lancet Respir Med. 2017]
11.Review Gamma interferon release assays for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
[Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014]
12.Specific detection of tuberculosis infection: an interferon-gamma-based assay using new antigens.